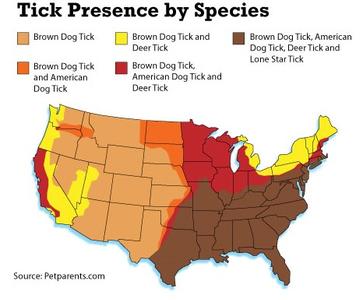
Domestic animals such as horses, cattle, dogs and even cats serve as substitute hosts for black-legged (deer) ticks.
Dogs
Prevention Tips:
- Vaccinate annually for Lyme disease – contracting Lyme disease doesn’t make them immune
- Apply a topical vet-recommended tick prevention
- Use a Scalibor collar as an alternative to topical protection
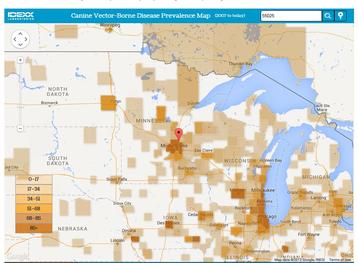
Prevalence Maps
Dogs & Lyme Disease Resources
- While Lyme disease is well known, it certainly isn’t the only disease that dogs—or people—can contract from ticks
- Seropositive Dogs Residing in an Endemic Area
- Ticks and Bird Dogs: The Minnesota – Field and Stream
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever diagnosed in metro dogs -MMCD
Horses



Troublesome Ticks – Protect Your Horse with Ease
Tick Borne Diseases in MN – University of MN Extension
Protects horses from flies, gnats, mosquitoes and TICKS! – Equi-Spot click on link to view video on how to apply Repel-X® Insecticide & Repellent
Cats Get Lyme Too
Key Points Regarding Lyme Disease in Dogs and Cats – CDC
Lyme Disease in Cats: cat-health-guide.org
Q Fever
Q fever is most often spread to people from inhalation of contaminated aerosols and dust from infected goats, sheep, cattle, and their environments. People can be infected by breathing contaminated dust from infected farms located miles away. Less commonly, people can get Q fever from drinking unpasteurized milk or from tick bites. Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists
BARTONELLOSIS: THE HIDDEN EPIDEMIC! By Edward B. Breitschwerdt, DVM